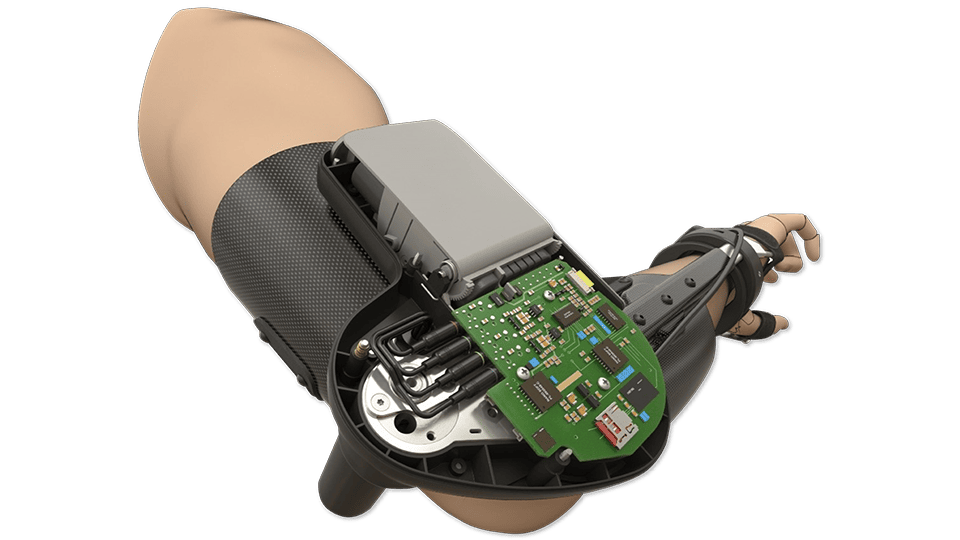
Industry 5.0 takes the innovation of Industry 4.0 a step further. Industry 5.0 focuses on optimizing production while emphasizing social and environmental benefit. The collaboration between humans and intelligent machines intensifies as the relationship between the two becomes more direct. Much like Industry 4.0, Industry 5.0 continues to prioritize automation, artificial intelligence, and augmented/virtual realities, but pushes these concepts further by considering with new depth the ways in which these technologies and integrated systems function in everyday life in a way that holistically enhances our day-to-day experiences, both virtually and physically.
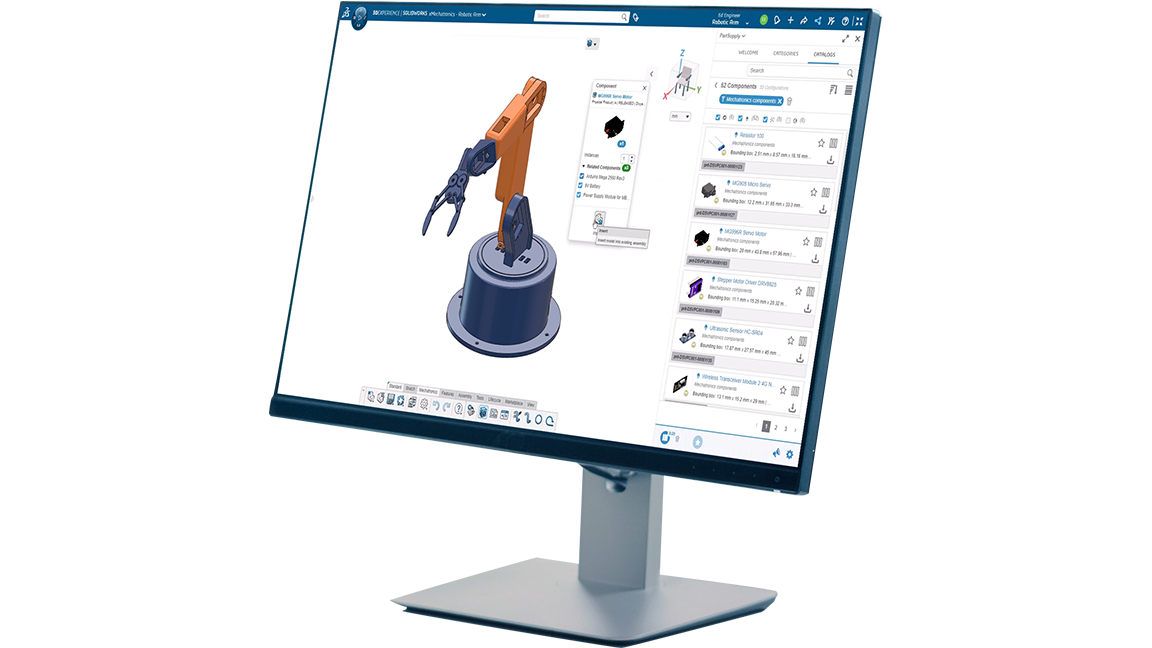
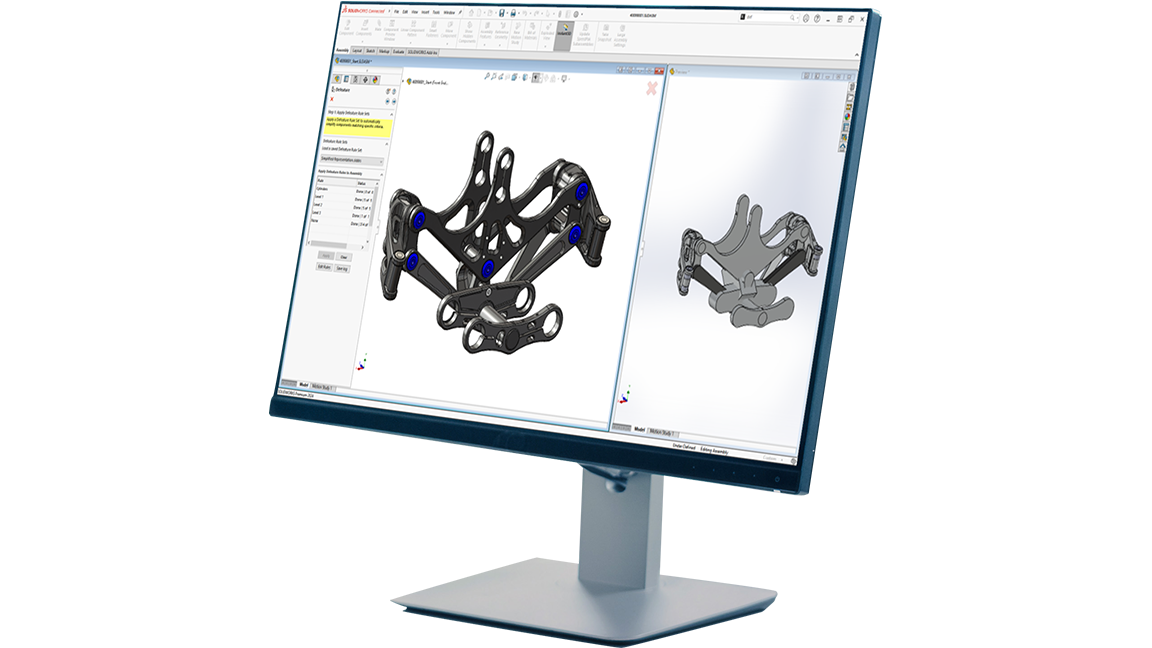
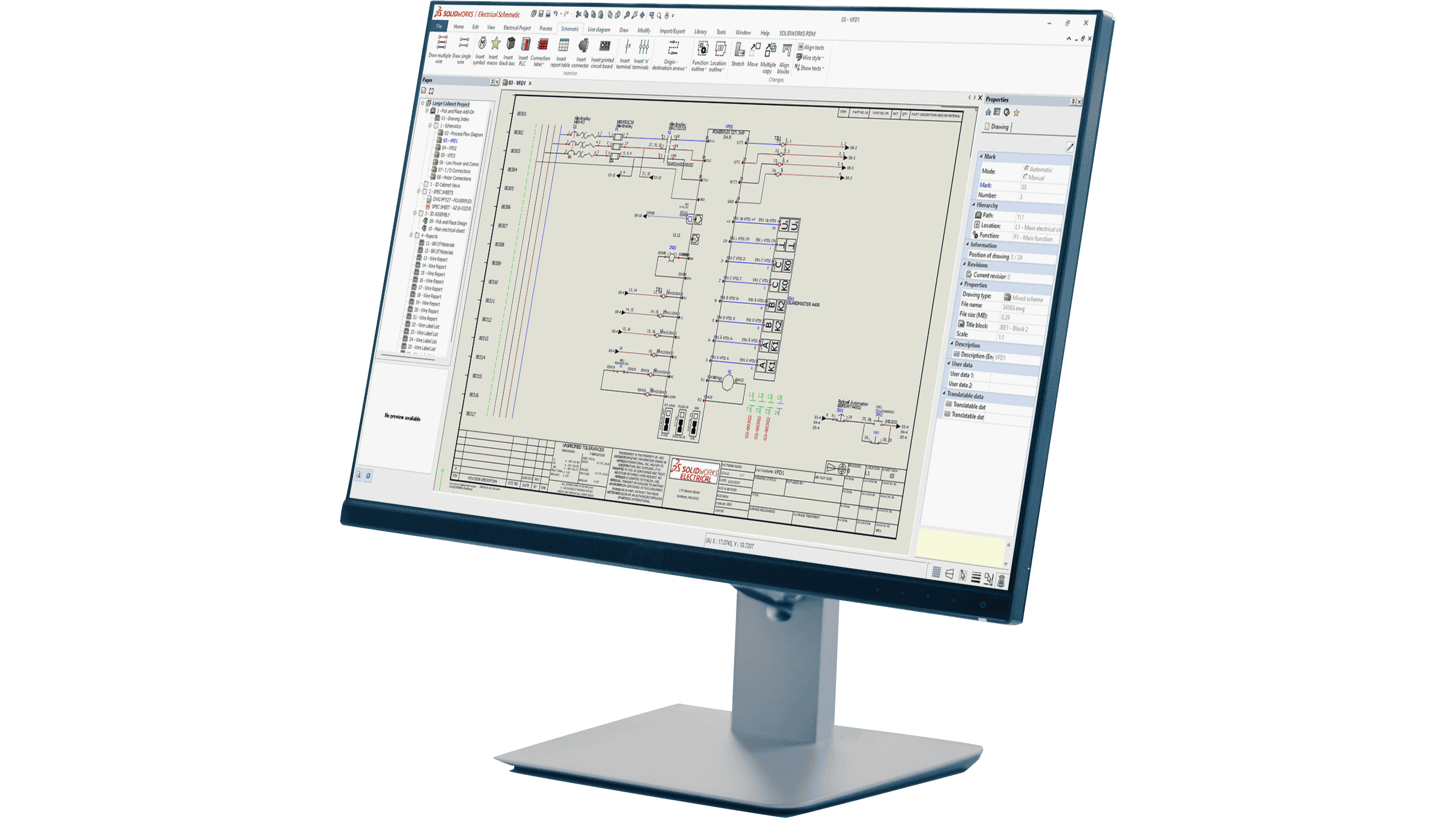
As we move into Industry 5.0, application of mechatronics will continue to play an integral role in driving the development of new, integrated technologies, thus facilitating this transition between technological eras. As technologies and integrated systems grow increasingly complex, the need for interdisciplinary design and collaboration also grows. Mechatronics as a field encapsulates this multidisciplinary approach to product design and innovation, making it a fantastic example of the types of projects we will increasingly see in demand as we continue into Industry 5.0.